10 Minutes to pandas¶
This is a short introduction to pandas, geared mainly for new users. You can see more complex recipes in the Cookbook
Customarily, we import as follows
In [1]: import pandas as pd
In [2]: import numpy as np
In [3]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Object Creation¶
See the Data Structure Intro section
Creating a Series by passing a list of values, letting pandas create a default integer index:
In [4]: s = pd.Series([1,3,5,np.nan,6,8])
In [5]: s
Out[5]:
0 1
1 3
2 5
3 NaN
4 6
5 8
dtype: float64
Creating a DataFrame by passing a numpy array, with a datetime index and labeled columns:
In [6]: dates = pd.date_range('20130101', periods=6)
In [7]: dates
Out[7]:
DatetimeIndex(['2013-01-01', '2013-01-02', '2013-01-03', '2013-01-04',
'2013-01-05', '2013-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D', tz=None)
In [8]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4), index=dates, columns=list('ABCD'))
In [9]: df
Out[9]:
A B C D
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988
Creating a DataFrame by passing a dict of objects that can be converted to series-like.
In [10]: df2 = pd.DataFrame({ 'A' : 1.,
....: 'B' : pd.Timestamp('20130102'),
....: 'C' : pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'),
....: 'D' : np.array([3] * 4,dtype='int32'),
....: 'E' : pd.Categorical(["test","train","test","train"]),
....: 'F' : 'foo' })
....:
In [11]: df2
Out[11]:
A B C D E F
0 1 2013-01-02 1 3 test foo
1 1 2013-01-02 1 3 train foo
2 1 2013-01-02 1 3 test foo
3 1 2013-01-02 1 3 train foo
Having specific dtypes
In [12]: df2.dtypes
Out[12]:
A float64
B datetime64[ns]
C float32
D int32
E category
F object
dtype: object
If you’re using IPython, tab completion for column names (as well as public attributes) is automatically enabled. Here’s a subset of the attributes that will be completed:
In [13]: df2.<TAB>
df2.A df2.boxplot
df2.abs df2.C
df2.add df2.clip
df2.add_prefix df2.clip_lower
df2.add_suffix df2.clip_upper
df2.align df2.columns
df2.all df2.combine
df2.any df2.combineAdd
df2.append df2.combine_first
df2.apply df2.combineMult
df2.applymap df2.compound
df2.as_blocks df2.consolidate
df2.asfreq df2.convert_objects
df2.as_matrix df2.copy
df2.astype df2.corr
df2.at df2.corrwith
df2.at_time df2.count
df2.axes df2.cov
df2.B df2.cummax
df2.between_time df2.cummin
df2.bfill df2.cumprod
df2.blocks df2.cumsum
df2.bool df2.D
As you can see, the columns A, B, C, and D are automatically tab completed. E is there as well; the rest of the attributes have been truncated for brevity.
Viewing Data¶
See the Basics section
See the top & bottom rows of the frame
In [14]: df.head()
Out[14]:
A B C D
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401
In [15]: df.tail(3)
Out[15]:
A B C D
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988
Display the index, columns, and the underlying numpy data
In [16]: df.index
Out[16]:
DatetimeIndex(['2013-01-01', '2013-01-02', '2013-01-03', '2013-01-04',
'2013-01-05', '2013-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D', tz=None)
In [17]: df.columns
Out[17]: Index([u'A', u'B', u'C', u'D'], dtype='object')
In [18]: df.values
Out[18]:
array([[ 0.4691, -0.2829, -1.5091, -1.1356],
[ 1.2121, -0.1732, 0.1192, -1.0442],
[-0.8618, -2.1046, -0.4949, 1.0718],
[ 0.7216, -0.7068, -1.0396, 0.2719],
[-0.425 , 0.567 , 0.2762, -1.0874],
[-0.6737, 0.1136, -1.4784, 0.525 ]])
Describe shows a quick statistic summary of your data
In [19]: df.describe()
Out[19]:
A B C D
count 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000
mean 0.073711 -0.431125 -0.687758 -0.233103
std 0.843157 0.922818 0.779887 0.973118
min -0.861849 -2.104569 -1.509059 -1.135632
25% -0.611510 -0.600794 -1.368714 -1.076610
50% 0.022070 -0.228039 -0.767252 -0.386188
75% 0.658444 0.041933 -0.034326 0.461706
max 1.212112 0.567020 0.276232 1.071804
Transposing your data
In [20]: df.T
Out[20]:
2013-01-01 2013-01-02 2013-01-03 2013-01-04 2013-01-05 2013-01-06
A 0.469112 1.212112 -0.861849 0.721555 -0.424972 -0.673690
B -0.282863 -0.173215 -2.104569 -0.706771 0.567020 0.113648
C -1.509059 0.119209 -0.494929 -1.039575 0.276232 -1.478427
D -1.135632 -1.044236 1.071804 0.271860 -1.087401 0.524988
Sorting by an axis
In [21]: df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False)
Out[21]:
D C B A
2013-01-01 -1.135632 -1.509059 -0.282863 0.469112
2013-01-02 -1.044236 0.119209 -0.173215 1.212112
2013-01-03 1.071804 -0.494929 -2.104569 -0.861849
2013-01-04 0.271860 -1.039575 -0.706771 0.721555
2013-01-05 -1.087401 0.276232 0.567020 -0.424972
2013-01-06 0.524988 -1.478427 0.113648 -0.673690
Sorting by values
In [22]: df.sort(columns='B')
Out[22]:
A B C D
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401
Selection¶
Note
While standard Python / Numpy expressions for selecting and setting are intuitive and come in handy for interactive work, for production code, we recommend the optimized pandas data access methods, .at, .iat, .loc, .iloc and .ix.
See the indexing documentation Indexing and Selecing Data and MultiIndex / Advanced Indexing
Getting¶
Selecting a single column, which yields a Series, equivalent to df.A
In [23]: df['A']
Out[23]:
2013-01-01 0.469112
2013-01-02 1.212112
2013-01-03 -0.861849
2013-01-04 0.721555
2013-01-05 -0.424972
2013-01-06 -0.673690
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: float64
Selecting via [], which slices the rows.
In [24]: df[0:3]
Out[24]:
A B C D
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
In [25]: df['20130102':'20130104']
Out[25]:
A B C D
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
Selection by Label¶
See more in Selection by Label
For getting a cross section using a label
In [26]: df.loc[dates[0]]
Out[26]:
A 0.469112
B -0.282863
C -1.509059
D -1.135632
Name: 2013-01-01 00:00:00, dtype: float64
Selecting on a multi-axis by label
In [27]: df.loc[:,['A','B']]
Out[27]:
A B
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648
Showing label slicing, both endpoints are included
In [28]: df.loc['20130102':'20130104',['A','B']]
Out[28]:
A B
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771
Reduction in the dimensions of the returned object
In [29]: df.loc['20130102',['A','B']]
Out[29]:
A 1.212112
B -0.173215
Name: 2013-01-02 00:00:00, dtype: float64
For getting a scalar value
In [30]: df.loc[dates[0],'A']
Out[30]: 0.46911229990718628
For getting fast access to a scalar (equiv to the prior method)
In [31]: df.at[dates[0],'A']
Out[31]: 0.46911229990718628
Selection by Position¶
See more in Selection by Position
Select via the position of the passed integers
In [32]: df.iloc[3]
Out[32]:
A 0.721555
B -0.706771
C -1.039575
D 0.271860
Name: 2013-01-04 00:00:00, dtype: float64
By integer slices, acting similar to numpy/python
In [33]: df.iloc[3:5,0:2]
Out[33]:
A B
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020
By lists of integer position locations, similar to the numpy/python style
In [34]: df.iloc[[1,2,4],[0,2]]
Out[34]:
A C
2013-01-02 1.212112 0.119209
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -0.494929
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.276232
For slicing rows explicitly
In [35]: df.iloc[1:3,:]
Out[35]:
A B C D
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804
For slicing columns explicitly
In [36]: df.iloc[:,1:3]
Out[36]:
B C
2013-01-01 -0.282863 -1.509059
2013-01-02 -0.173215 0.119209
2013-01-03 -2.104569 -0.494929
2013-01-04 -0.706771 -1.039575
2013-01-05 0.567020 0.276232
2013-01-06 0.113648 -1.478427
For getting a value explicitly
In [37]: df.iloc[1,1]
Out[37]: -0.17321464905330858
For getting fast access to a scalar (equiv to the prior method)
In [38]: df.iat[1,1]
Out[38]: -0.17321464905330858
Boolean Indexing¶
Using a single column’s values to select data.
In [39]: df[df.A > 0]
Out[39]:
A B C D
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860
A where operation for getting.
In [40]: df[df > 0]
Out[40]:
A B C D
2013-01-01 0.469112 NaN NaN NaN
2013-01-02 1.212112 NaN 0.119209 NaN
2013-01-03 NaN NaN NaN 1.071804
2013-01-04 0.721555 NaN NaN 0.271860
2013-01-05 NaN 0.567020 0.276232 NaN
2013-01-06 NaN 0.113648 NaN 0.524988
Using the isin() method for filtering:
In [41]: df2 = df.copy()
In [42]: df2['E'] = ['one', 'one','two','three','four','three']
In [43]: df2
Out[43]:
A B C D E
2013-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059 -1.135632 one
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 -1.044236 one
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804 two
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 0.271860 three
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401 four
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988 three
In [44]: df2[df2['E'].isin(['two','four'])]
Out[44]:
A B C D E
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 1.071804 two
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 -1.087401 four
Setting¶
Setting a new column automatically aligns the data by the indexes
In [45]: s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6], index=pd.date_range('20130102', periods=6))
In [46]: s1
Out[46]:
2013-01-02 1
2013-01-03 2
2013-01-04 3
2013-01-05 4
2013-01-06 5
2013-01-07 6
Freq: D, dtype: int64
In [47]: df['F'] = s1
Setting values by label
In [48]: df.at[dates[0],'A'] = 0
Setting values by position
In [49]: df.iat[0,1] = 0
Setting by assigning with a numpy array
In [50]: df.loc[:,'D'] = np.array([5] * len(df))
The result of the prior setting operations
In [51]: df
Out[51]:
A B C D F
2013-01-01 0.000000 0.000000 -1.509059 5 NaN
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 5 1
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 5 2
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 5 3
2013-01-05 -0.424972 0.567020 0.276232 5 4
2013-01-06 -0.673690 0.113648 -1.478427 5 5
A where operation with setting.
In [52]: df2 = df.copy()
In [53]: df2[df2 > 0] = -df2
In [54]: df2
Out[54]:
A B C D F
2013-01-01 0.000000 0.000000 -1.509059 -5 NaN
2013-01-02 -1.212112 -0.173215 -0.119209 -5 -1
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 -5 -2
2013-01-04 -0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 -5 -3
2013-01-05 -0.424972 -0.567020 -0.276232 -5 -4
2013-01-06 -0.673690 -0.113648 -1.478427 -5 -5
Missing Data¶
pandas primarily uses the value np.nan to represent missing data. It is by default not included in computations. See the Missing Data section
Reindexing allows you to change/add/delete the index on a specified axis. This returns a copy of the data.
In [55]: df1 = df.reindex(index=dates[0:4], columns=list(df.columns) + ['E'])
In [56]: df1.loc[dates[0]:dates[1],'E'] = 1
In [57]: df1
Out[57]:
A B C D F E
2013-01-01 0.000000 0.000000 -1.509059 5 NaN 1
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 5 1 1
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 5 2 NaN
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 5 3 NaN
To drop any rows that have missing data.
In [58]: df1.dropna(how='any')
Out[58]:
A B C D F E
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 5 1 1
Filling missing data
In [59]: df1.fillna(value=5)
Out[59]:
A B C D F E
2013-01-01 0.000000 0.000000 -1.509059 5 5 1
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 0.119209 5 1 1
2013-01-03 -0.861849 -2.104569 -0.494929 5 2 5
2013-01-04 0.721555 -0.706771 -1.039575 5 3 5
To get the boolean mask where values are nan
In [60]: pd.isnull(df1)
Out[60]:
A B C D F E
2013-01-01 False False False False True False
2013-01-02 False False False False False False
2013-01-03 False False False False False True
2013-01-04 False False False False False True
Operations¶
See the Basic section on Binary Ops
Stats¶
Operations in general exclude missing data.
Performing a descriptive statistic
In [61]: df.mean()
Out[61]:
A -0.004474
B -0.383981
C -0.687758
D 5.000000
F 3.000000
dtype: float64
Same operation on the other axis
In [62]: df.mean(1)
Out[62]:
2013-01-01 0.872735
2013-01-02 1.431621
2013-01-03 0.707731
2013-01-04 1.395042
2013-01-05 1.883656
2013-01-06 1.592306
Freq: D, dtype: float64
Operating with objects that have different dimensionality and need alignment. In addition, pandas automatically broadcasts along the specified dimension.
In [63]: s = pd.Series([1,3,5,np.nan,6,8], index=dates).shift(2)
In [64]: s
Out[64]:
2013-01-01 NaN
2013-01-02 NaN
2013-01-03 1
2013-01-04 3
2013-01-05 5
2013-01-06 NaN
Freq: D, dtype: float64
In [65]: df.sub(s, axis='index')
Out[65]:
A B C D F
2013-01-01 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2013-01-02 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2013-01-03 -1.861849 -3.104569 -1.494929 4 1
2013-01-04 -2.278445 -3.706771 -4.039575 2 0
2013-01-05 -5.424972 -4.432980 -4.723768 0 -1
2013-01-06 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
Apply¶
Applying functions to the data
In [66]: df.apply(np.cumsum)
Out[66]:
A B C D F
2013-01-01 0.000000 0.000000 -1.509059 5 NaN
2013-01-02 1.212112 -0.173215 -1.389850 10 1
2013-01-03 0.350263 -2.277784 -1.884779 15 3
2013-01-04 1.071818 -2.984555 -2.924354 20 6
2013-01-05 0.646846 -2.417535 -2.648122 25 10
2013-01-06 -0.026844 -2.303886 -4.126549 30 15
In [67]: df.apply(lambda x: x.max() - x.min())
Out[67]:
A 2.073961
B 2.671590
C 1.785291
D 0.000000
F 4.000000
dtype: float64
Histogramming¶
See more at Histogramming and Discretization
In [68]: s = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 7, size=10))
In [69]: s
Out[69]:
0 4
1 2
2 1
3 2
4 6
5 4
6 4
7 6
8 4
9 4
dtype: int32
In [70]: s.value_counts()
Out[70]:
4 5
6 2
2 2
1 1
dtype: int64
String Methods¶
Series is equipped with a set of string processing methods in the str attribute that make it easy to operate on each element of the array, as in the code snippet below. Note that pattern-matching in str generally uses regular expressions by default (and in some cases always uses them). See more at Vectorized String Methods.
In [71]: s = pd.Series(['A', 'B', 'C', 'Aaba', 'Baca', np.nan, 'CABA', 'dog', 'cat'])
In [72]: s.str.lower()
Out[72]:
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 aaba
4 baca
5 NaN
6 caba
7 dog
8 cat
dtype: object
Merge¶
Concat¶
pandas provides various facilities for easily combining together Series, DataFrame, and Panel objects with various kinds of set logic for the indexes and relational algebra functionality in the case of join / merge-type operations.
See the Merging section
Concatenating pandas objects together with concat():
In [73]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4))
In [74]: df
Out[74]:
0 1 2 3
0 -0.548702 1.467327 -1.015962 -0.483075
1 1.637550 -1.217659 -0.291519 -1.745505
2 -0.263952 0.991460 -0.919069 0.266046
3 -0.709661 1.669052 1.037882 -1.705775
4 -0.919854 -0.042379 1.247642 -0.009920
5 0.290213 0.495767 0.362949 1.548106
6 -1.131345 -0.089329 0.337863 -0.945867
7 -0.932132 1.956030 0.017587 -0.016692
8 -0.575247 0.254161 -1.143704 0.215897
9 1.193555 -0.077118 -0.408530 -0.862495
# break it into pieces
In [75]: pieces = [df[:3], df[3:7], df[7:]]
In [76]: pd.concat(pieces)
Out[76]:
0 1 2 3
0 -0.548702 1.467327 -1.015962 -0.483075
1 1.637550 -1.217659 -0.291519 -1.745505
2 -0.263952 0.991460 -0.919069 0.266046
3 -0.709661 1.669052 1.037882 -1.705775
4 -0.919854 -0.042379 1.247642 -0.009920
5 0.290213 0.495767 0.362949 1.548106
6 -1.131345 -0.089329 0.337863 -0.945867
7 -0.932132 1.956030 0.017587 -0.016692
8 -0.575247 0.254161 -1.143704 0.215897
9 1.193555 -0.077118 -0.408530 -0.862495
Join¶
SQL style merges. See the Database style joining
In [77]: left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'foo'], 'lval': [1, 2]})
In [78]: right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'foo'], 'rval': [4, 5]})
In [79]: left
Out[79]:
key lval
0 foo 1
1 foo 2
In [80]: right
Out[80]:
key rval
0 foo 4
1 foo 5
In [81]: pd.merge(left, right, on='key')
Out[81]:
key lval rval
0 foo 1 4
1 foo 1 5
2 foo 2 4
3 foo 2 5
Append¶
Append rows to a dataframe. See the Appending
In [82]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(8, 4), columns=['A','B','C','D'])
In [83]: df
Out[83]:
A B C D
0 1.346061 1.511763 1.627081 -0.990582
1 -0.441652 1.211526 0.268520 0.024580
2 -1.577585 0.396823 -0.105381 -0.532532
3 1.453749 1.208843 -0.080952 -0.264610
4 -0.727965 -0.589346 0.339969 -0.693205
5 -0.339355 0.593616 0.884345 1.591431
6 0.141809 0.220390 0.435589 0.192451
7 -0.096701 0.803351 1.715071 -0.708758
In [84]: s = df.iloc[3]
In [85]: df.append(s, ignore_index=True)
Out[85]:
A B C D
0 1.346061 1.511763 1.627081 -0.990582
1 -0.441652 1.211526 0.268520 0.024580
2 -1.577585 0.396823 -0.105381 -0.532532
3 1.453749 1.208843 -0.080952 -0.264610
4 -0.727965 -0.589346 0.339969 -0.693205
5 -0.339355 0.593616 0.884345 1.591431
6 0.141809 0.220390 0.435589 0.192451
7 -0.096701 0.803351 1.715071 -0.708758
8 1.453749 1.208843 -0.080952 -0.264610
Grouping¶
By “group by” we are referring to a process involving one or more of the following steps
- Splitting the data into groups based on some criteria
- Applying a function to each group independently
- Combining the results into a data structure
See the Grouping section
In [86]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A' : ['foo', 'bar', 'foo', 'bar',
....: 'foo', 'bar', 'foo', 'foo'],
....: 'B' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three',
....: 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
....: 'C' : np.random.randn(8),
....: 'D' : np.random.randn(8)})
....:
In [87]: df
Out[87]:
A B C D
0 foo one -1.202872 -0.055224
1 bar one -1.814470 2.395985
2 foo two 1.018601 1.552825
3 bar three -0.595447 0.166599
4 foo two 1.395433 0.047609
5 bar two -0.392670 -0.136473
6 foo one 0.007207 -0.561757
7 foo three 1.928123 -1.623033
Grouping and then applying a function sum to the resulting groups.
In [88]: df.groupby('A').sum()
Out[88]:
C D
A
bar -2.802588 2.42611
foo 3.146492 -0.63958
Grouping by multiple columns forms a hierarchical index, which we then apply the function.
In [89]: df.groupby(['A','B']).sum()
Out[89]:
C D
A B
bar one -1.814470 2.395985
three -0.595447 0.166599
two -0.392670 -0.136473
foo one -1.195665 -0.616981
three 1.928123 -1.623033
two 2.414034 1.600434
Reshaping¶
See the sections on Hierarchical Indexing and Reshaping.
Stack¶
In [90]: tuples = list(zip(*[['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz',
....: 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'],
....: ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two',
....: 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]))
....:
In [91]: index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(tuples, names=['first', 'second'])
In [92]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(8, 2), index=index, columns=['A', 'B'])
In [93]: df2 = df[:4]
In [94]: df2
Out[94]:
A B
first second
bar one 0.029399 -0.542108
two 0.282696 -0.087302
baz one -1.575170 1.771208
two 0.816482 1.100230
The stack() method “compresses” a level in the DataFrame’s columns.
In [95]: stacked = df2.stack()
In [96]: stacked
Out[96]:
first second
bar one A 0.029399
B -0.542108
two A 0.282696
B -0.087302
baz one A -1.575170
B 1.771208
two A 0.816482
B 1.100230
dtype: float64
With a “stacked” DataFrame or Series (having a MultiIndex as the index), the inverse operation of stack() is unstack(), which by default unstacks the last level:
In [97]: stacked.unstack()
Out[97]:
A B
first second
bar one 0.029399 -0.542108
two 0.282696 -0.087302
baz one -1.575170 1.771208
two 0.816482 1.100230
In [98]: stacked.unstack(1)
Out[98]:
second one two
first
bar A 0.029399 0.282696
B -0.542108 -0.087302
baz A -1.575170 0.816482
B 1.771208 1.100230
In [99]: stacked.unstack(0)
Out[99]:
first bar baz
second
one A 0.029399 -1.575170
B -0.542108 1.771208
two A 0.282696 0.816482
B -0.087302 1.100230
Pivot Tables¶
See the section on Pivot Tables.
In [100]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three'] * 3,
.....: 'B' : ['A', 'B', 'C'] * 4,
.....: 'C' : ['foo', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'bar'] * 2,
.....: 'D' : np.random.randn(12),
.....: 'E' : np.random.randn(12)})
.....:
In [101]: df
Out[101]:
A B C D E
0 one A foo 1.418757 -0.179666
1 one B foo -1.879024 1.291836
2 two C foo 0.536826 -0.009614
3 three A bar 1.006160 0.392149
4 one B bar -0.029716 0.264599
5 one C bar -1.146178 -0.057409
6 two A foo 0.100900 -1.425638
7 three B foo -1.035018 1.024098
8 one C foo 0.314665 -0.106062
9 one A bar -0.773723 1.824375
10 two B bar -1.170653 0.595974
11 three C bar 0.648740 1.167115
We can produce pivot tables from this data very easily:
In [102]: pd.pivot_table(df, values='D', index=['A', 'B'], columns=['C'])
Out[102]:
C bar foo
A B
one A -0.773723 1.418757
B -0.029716 -1.879024
C -1.146178 0.314665
three A 1.006160 NaN
B NaN -1.035018
C 0.648740 NaN
two A NaN 0.100900
B -1.170653 NaN
C NaN 0.536826
Time Series¶
pandas has simple, powerful, and efficient functionality for performing resampling operations during frequency conversion (e.g., converting secondly data into 5-minutely data). This is extremely common in, but not limited to, financial applications. See the Time Series section
In [103]: rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2012', periods=100, freq='S')
In [104]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 500, len(rng)), index=rng)
In [105]: ts.resample('5Min', how='sum')
Out[105]:
2012-01-01 25083
Freq: 5T, dtype: int32
Time zone representation
In [106]: rng = pd.date_range('3/6/2012 00:00', periods=5, freq='D')
In [107]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(rng)), rng)
In [108]: ts
Out[108]:
2012-03-06 0.464000
2012-03-07 0.227371
2012-03-08 -0.496922
2012-03-09 0.306389
2012-03-10 -2.290613
Freq: D, dtype: float64
In [109]: ts_utc = ts.tz_localize('UTC')
In [110]: ts_utc
Out[110]:
2012-03-06 00:00:00+00:00 0.464000
2012-03-07 00:00:00+00:00 0.227371
2012-03-08 00:00:00+00:00 -0.496922
2012-03-09 00:00:00+00:00 0.306389
2012-03-10 00:00:00+00:00 -2.290613
Freq: D, dtype: float64
Convert to another time zone
In [111]: ts_utc.tz_convert('US/Eastern')
Out[111]:
2012-03-05 19:00:00-05:00 0.464000
2012-03-06 19:00:00-05:00 0.227371
2012-03-07 19:00:00-05:00 -0.496922
2012-03-08 19:00:00-05:00 0.306389
2012-03-09 19:00:00-05:00 -2.290613
Freq: D, dtype: float64
Converting between time span representations
In [112]: rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2012', periods=5, freq='M')
In [113]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(rng)), index=rng)
In [114]: ts
Out[114]:
2012-01-31 -1.134623
2012-02-29 -1.561819
2012-03-31 -0.260838
2012-04-30 0.281957
2012-05-31 1.523962
Freq: M, dtype: float64
In [115]: ps = ts.to_period()
In [116]: ps
Out[116]:
2012-01 -1.134623
2012-02 -1.561819
2012-03 -0.260838
2012-04 0.281957
2012-05 1.523962
Freq: M, dtype: float64
In [117]: ps.to_timestamp()
Out[117]:
2012-01-01 -1.134623
2012-02-01 -1.561819
2012-03-01 -0.260838
2012-04-01 0.281957
2012-05-01 1.523962
Freq: MS, dtype: float64
Converting between period and timestamp enables some convenient arithmetic functions to be used. In the following example, we convert a quarterly frequency with year ending in November to 9am of the end of the month following the quarter end:
In [118]: prng = pd.period_range('1990Q1', '2000Q4', freq='Q-NOV')
In [119]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(prng)), prng)
In [120]: ts.index = (prng.asfreq('M', 'e') + 1).asfreq('H', 's') + 9
In [121]: ts.head()
Out[121]:
1990-03-01 09:00 -0.902937
1990-06-01 09:00 0.068159
1990-09-01 09:00 -0.057873
1990-12-01 09:00 -0.368204
1991-03-01 09:00 -1.144073
Freq: H, dtype: float64
Categoricals¶
Since version 0.15, pandas can include categorical data in a DataFrame. For full docs, see the categorical introduction and the API documentation.
In [122]: df = pd.DataFrame({"id":[1,2,3,4,5,6], "raw_grade":['a', 'b', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'e']})
Convert the raw grades to a categorical data type.
In [123]: df["grade"] = df["raw_grade"].astype("category")
In [124]: df["grade"]
Out[124]:
0 a
1 b
2 b
3 a
4 a
5 e
Name: grade, dtype: category
Categories (3, object): [a, b, e]
Rename the categories to more meaningful names (assigning to Series.cat.categories is inplace!)
In [125]: df["grade"].cat.categories = ["very good", "good", "very bad"]
Reorder the categories and simultaneously add the missing categories (methods under Series .cat return a new Series per default).
In [126]: df["grade"] = df["grade"].cat.set_categories(["very bad", "bad", "medium", "good", "very good"])
In [127]: df["grade"]
Out[127]:
0 very good
1 good
2 good
3 very good
4 very good
5 very bad
Name: grade, dtype: category
Categories (5, object): [very bad, bad, medium, good, very good]
Sorting is per order in the categories, not lexical order.
In [128]: df.sort("grade")
Out[128]:
id raw_grade grade
5 6 e very bad
1 2 b good
2 3 b good
0 1 a very good
3 4 a very good
4 5 a very good
Grouping by a categorical column shows also empty categories.
In [129]: df.groupby("grade").size()
Out[129]:
grade
very bad 1
bad NaN
medium NaN
good 2
very good 3
dtype: float64
Plotting¶
Plotting docs.
In [130]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000), index=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=1000))
In [131]: ts = ts.cumsum()
In [132]: ts.plot()
Out[132]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0xaf663c8c>
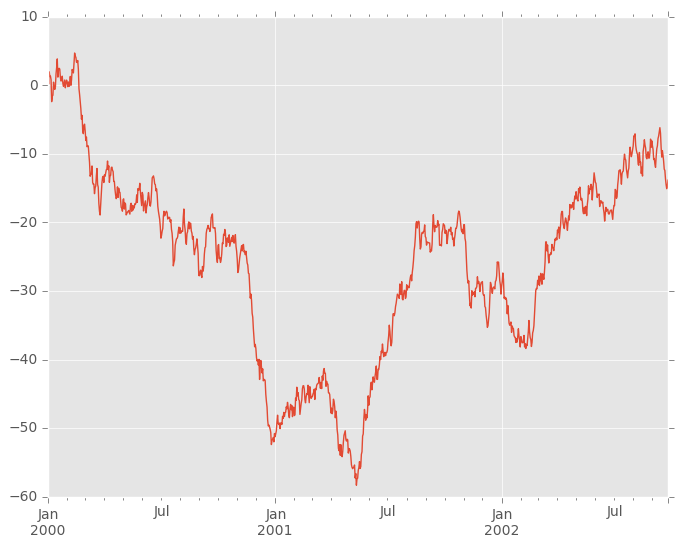
On DataFrame, plot() is a convenience to plot all of the columns with labels:
In [133]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4), index=ts.index,
.....: columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
.....:
In [134]: df = df.cumsum()
In [135]: plt.figure(); df.plot(); plt.legend(loc='best')
Out[135]: <matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0xaf5b31cc>
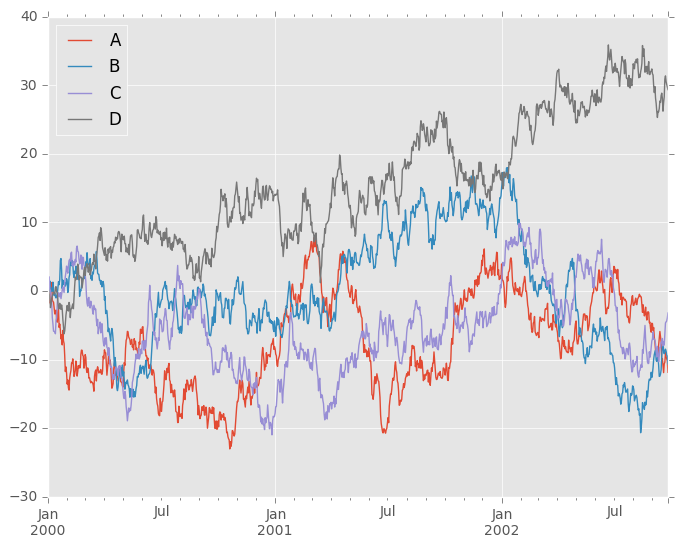
Getting Data In/Out¶
CSV¶
In [136]: df.to_csv('foo.csv')
In [137]: pd.read_csv('foo.csv')
Out[137]:
Unnamed: 0 A B C D
0 2000-01-01 0.266457 -0.399641 -0.219582 1.186860
1 2000-01-02 -1.170732 -0.345873 1.653061 -0.282953
2 2000-01-03 -1.734933 0.530468 2.060811 -0.515536
3 2000-01-04 -1.555121 1.452620 0.239859 -1.156896
4 2000-01-05 0.578117 0.511371 0.103552 -2.428202
5 2000-01-06 0.478344 0.449933 -0.741620 -1.962409
6 2000-01-07 1.235339 -0.091757 -1.543861 -1.084753
.. ... ... ... ... ...
993 2002-09-20 -10.628548 -9.153563 -7.883146 28.313940
994 2002-09-21 -10.390377 -8.727491 -6.399645 30.914107
995 2002-09-22 -8.985362 -8.485624 -4.669462 31.367740
996 2002-09-23 -9.558560 -8.781216 -4.499815 30.518439
997 2002-09-24 -9.902058 -9.340490 -4.386639 30.105593
998 2002-09-25 -10.216020 -9.480682 -3.933802 29.758560
999 2002-09-26 -11.856774 -10.671012 -3.216025 29.369368
[1000 rows x 5 columns]
HDF5¶
Reading and writing to HDFStores
Writing to a HDF5 Store
In [138]: df.to_hdf('foo.h5','df')
Reading from a HDF5 Store
In [139]: pd.read_hdf('foo.h5','df')
Out[139]:
A B C D
2000-01-01 0.266457 -0.399641 -0.219582 1.186860
2000-01-02 -1.170732 -0.345873 1.653061 -0.282953
2000-01-03 -1.734933 0.530468 2.060811 -0.515536
2000-01-04 -1.555121 1.452620 0.239859 -1.156896
2000-01-05 0.578117 0.511371 0.103552 -2.428202
2000-01-06 0.478344 0.449933 -0.741620 -1.962409
2000-01-07 1.235339 -0.091757 -1.543861 -1.084753
... ... ... ... ...
2002-09-20 -10.628548 -9.153563 -7.883146 28.313940
2002-09-21 -10.390377 -8.727491 -6.399645 30.914107
2002-09-22 -8.985362 -8.485624 -4.669462 31.367740
2002-09-23 -9.558560 -8.781216 -4.499815 30.518439
2002-09-24 -9.902058 -9.340490 -4.386639 30.105593
2002-09-25 -10.216020 -9.480682 -3.933802 29.758560
2002-09-26 -11.856774 -10.671012 -3.216025 29.369368
[1000 rows x 4 columns]
Excel¶
Reading and writing to MS Excel
Writing to an excel file
In [140]: df.to_excel('foo.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
Reading from an excel file
In [141]: pd.read_excel('foo.xlsx', 'Sheet1', index_col=None, na_values=['NA'])
Out[141]:
A B C D
2000-01-01 0.266457 -0.399641 -0.219582 1.186860
2000-01-02 -1.170732 -0.345873 1.653061 -0.282953
2000-01-03 -1.734933 0.530468 2.060811 -0.515536
2000-01-04 -1.555121 1.452620 0.239859 -1.156896
2000-01-05 0.578117 0.511371 0.103552 -2.428202
2000-01-06 0.478344 0.449933 -0.741620 -1.962409
2000-01-07 1.235339 -0.091757 -1.543861 -1.084753
... ... ... ... ...
2002-09-20 -10.628548 -9.153563 -7.883146 28.313940
2002-09-21 -10.390377 -8.727491 -6.399645 30.914107
2002-09-22 -8.985362 -8.485624 -4.669462 31.367740
2002-09-23 -9.558560 -8.781216 -4.499815 30.518439
2002-09-24 -9.902058 -9.340490 -4.386639 30.105593
2002-09-25 -10.216020 -9.480682 -3.933802 29.758560
2002-09-26 -11.856774 -10.671012 -3.216025 29.369368
[1000 rows x 4 columns]
Gotchas¶
If you are trying an operation and you see an exception like:
>>> if pd.Series([False, True, False]):
print("I was true")
Traceback
...
ValueError: The truth value of an array is ambiguous. Use a.empty, a.any() or a.all().
See Comparisons for an explanation and what to do.
See Gotchas as well.