Plotting with matplotlib¶
Note
We intend to build more plotting integration with matplotlib as time goes on.
We use the standard convention for referencing the matplotlib API:
In [870]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Basic plotting: plot¶
The plot method on Series and DataFrame is just a simple wrapper around plt.plot:
In [871]: ts = Series(randn(1000), index=DateRange('1/1/2000', periods=1000))
In [872]: ts = ts.cumsum()
In [873]: ts.plot()
Out[873]: <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x1165cb350>
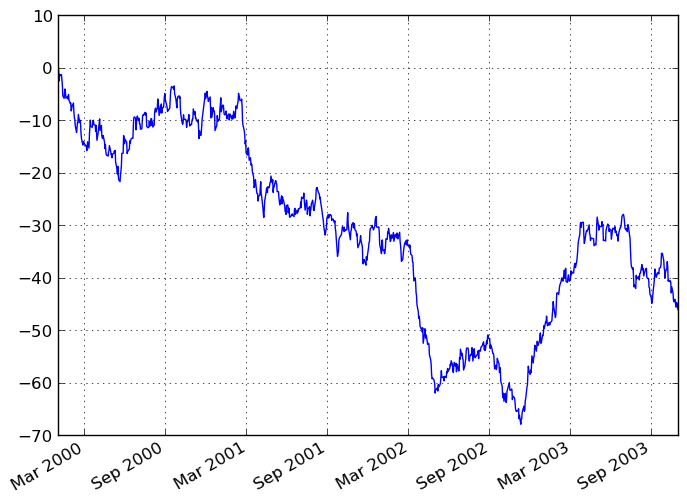
If the index consists of dates, it calls gca().autofmt_xdate() to try to format the x-axis nicely as per above. The method takes a number of arguments for controlling the look of the plot:
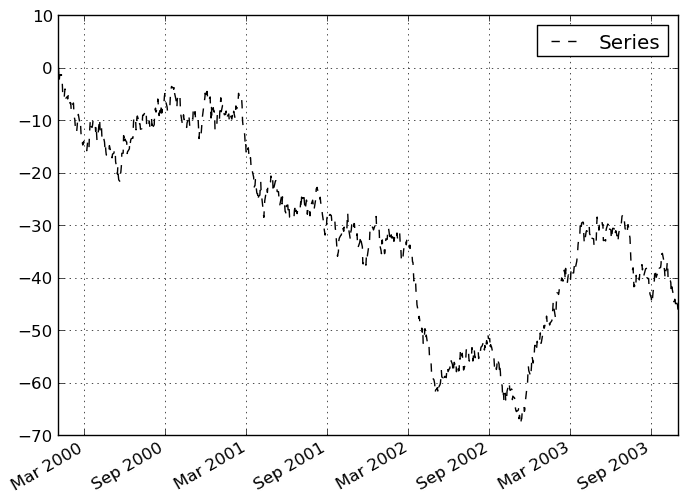
In [874]: plt.figure(); ts.plot(style='k--', label='Series'); plt.legend()
Out[874]: <matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x1197845d0>
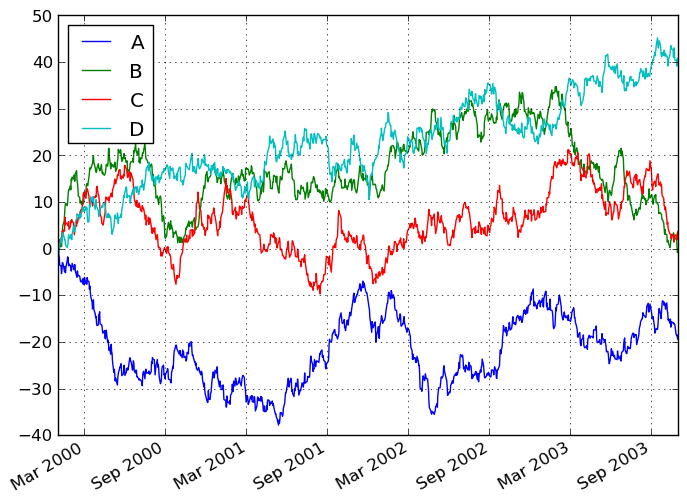
On DataFrame, plot is a convenience to plot all of the columns with labels:
In [875]: df = DataFrame(randn(1000, 4), index=ts.index,
.....: columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
In [876]: df = df.cumsum()
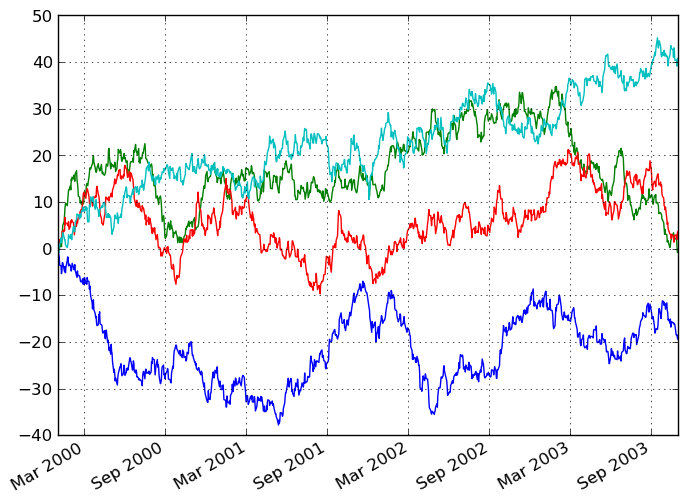
In [877]: plt.figure(); df.plot(); plt.legend(loc='best')
Out[877]: <matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x1197b3790>
You may set the legend argument to False to hide the legend, which is shown by default.
In [878]: df.plot(legend=False)
Out[878]: <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x11ad67b50>
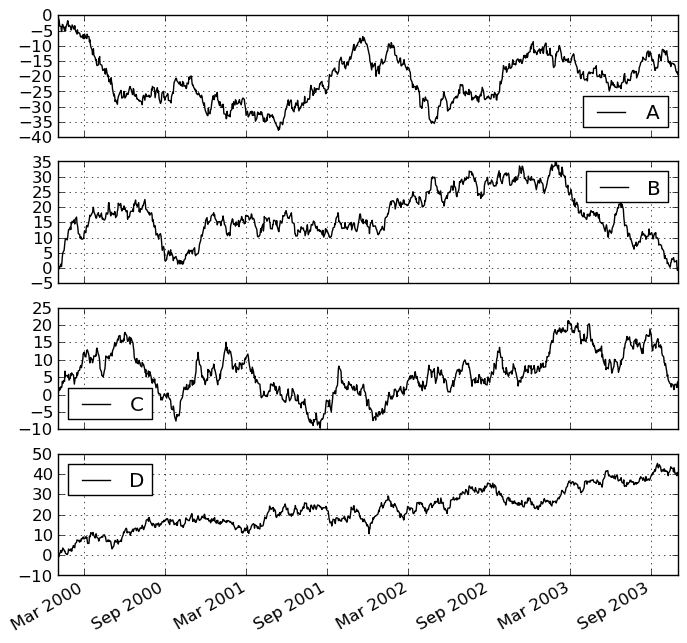
Some other options are available, like plotting each Series on a different axis:
In [879]: df.plot(subplots=True, figsize=(8, 8)); plt.legend(loc='best')
Out[879]: <matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x11ad6a0d0>
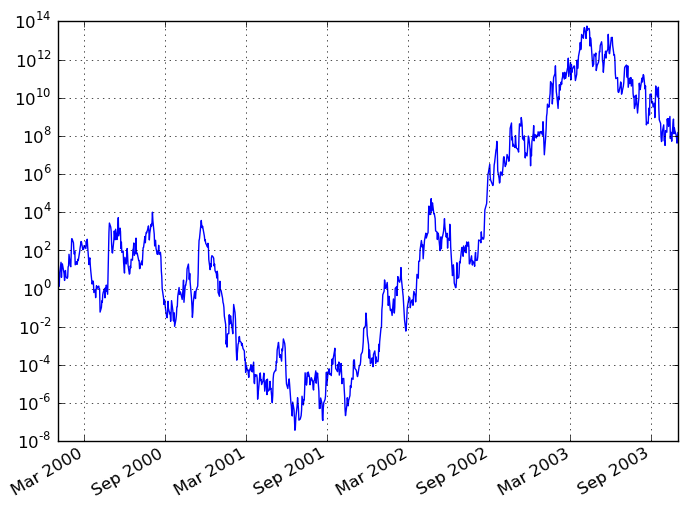
You may pass logy to get a log-scale Y axis.
In [880]: plt.figure();
In [880]: ts = Series(randn(1000), index=DateRange('1/1/2000', periods=1000))
In [881]: ts = np.exp(ts.cumsum())
In [882]: ts.plot(logy=True)
Out[882]: <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x11af94550>
Targeting different subplots¶
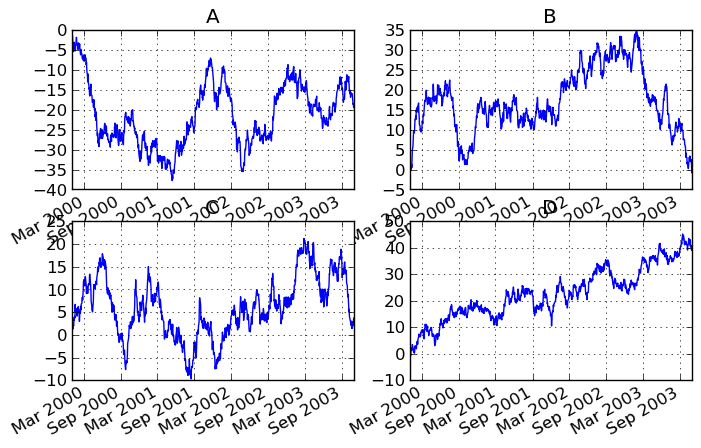
You can pass an ax argument to Series.plot to plot on a particular axis:
In [883]: fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(8, 5))
In [884]: df['A'].plot(ax=axes[0,0]); axes[0,0].set_title('A')
Out[884]: <matplotlib.text.Text at 0x11bc42510>
In [885]: df['B'].plot(ax=axes[0,1]); axes[0,1].set_title('B')
Out[885]: <matplotlib.text.Text at 0x11bdf2990>
In [886]: df['C'].plot(ax=axes[1,0]); axes[1,0].set_title('C')
Out[886]: <matplotlib.text.Text at 0x11bdd6c10>
In [887]: df['D'].plot(ax=axes[1,1]); axes[1,1].set_title('D')
Out[887]: <matplotlib.text.Text at 0x119735f50>
Other plotting features¶
Plotting non-time series data¶
For labeled, non-time series data, you may wish to produce a bar plot:
In [888]: plt.figure();
In [888]: df.ix[5].plot(kind='bar'); plt.axhline(0, color='k')
Out[888]: <matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x11bcf22d0>
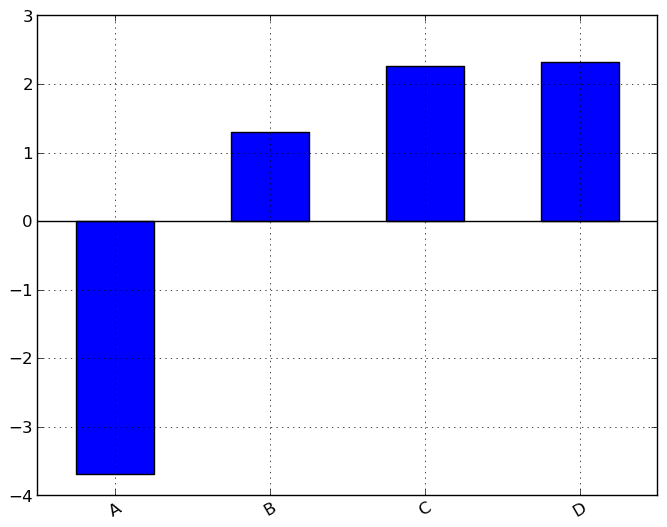
Histogramming¶
In [889]: plt.figure();
In [889]: df['A'].diff().hist()
Out[889]: <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x11bd233d0>
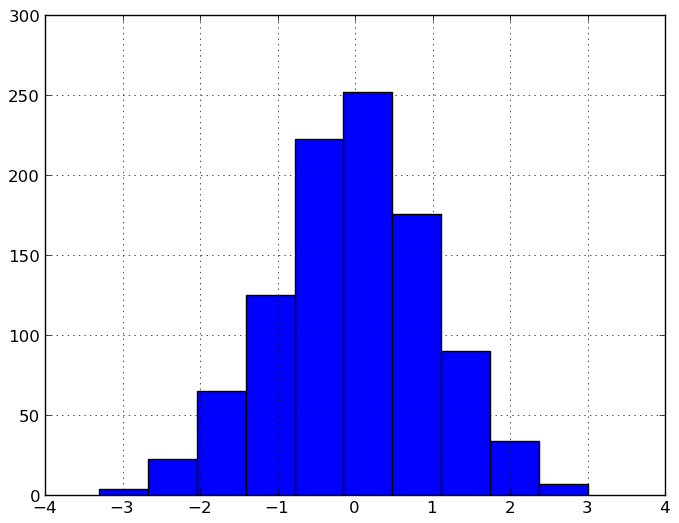
For a DataFrame, hist plots the histograms of the columns on multiple subplots:
In [890]: plt.figure()
Out[890]: <matplotlib.figure.Figure at 0x11bd55390>
In [891]: df.diff().hist(color='k', alpha=0.5, bins=50)
Out[891]:
array([[Axes(0.125,0.536364;0.352273x0.363636),
Axes(0.547727,0.536364;0.352273x0.363636)],
[Axes(0.125,0.1;0.352273x0.363636),
Axes(0.547727,0.1;0.352273x0.363636)]], dtype=object)
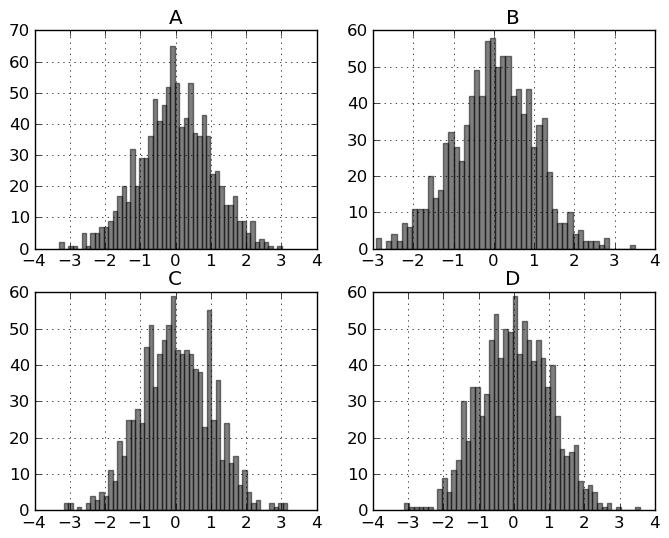
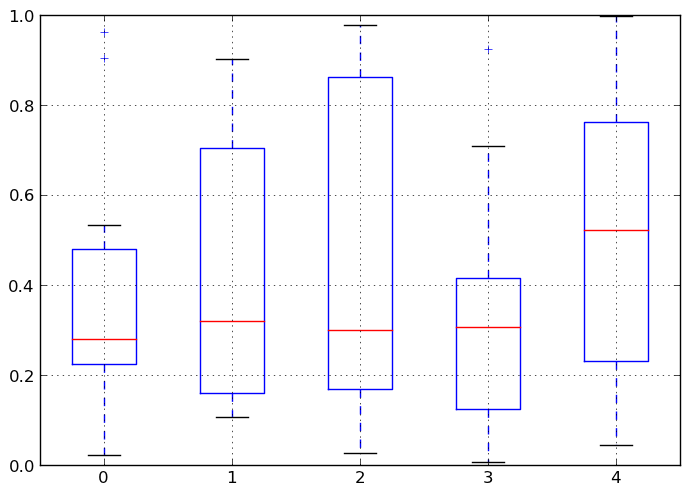
Box-Plotting¶
DataFrame has a boxplot method which allows you to visualize the distribution of values within each column.
For instance, here is a boxplot representing five trials of 10 observations of a uniform random variable on [0,1).
In [892]: df = DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,5))
In [893]: plt.figure();
In [893]: df.boxplot()
Out[893]: <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x11bd680d0>
You can create a stratified boxplot using the by keyword argument to create groupings. For instance,
In [894]: df = DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,2), columns=['Col1', 'Col2'] )
In [895]: df['X'] = Series(['A','A','A','A','A','B','B','B','B','B'])
In [896]: plt.figure();
In [896]: df.boxplot(by='X')
Out[896]: array([Axes(0.1,0.15;0.363636x0.75), Axes(0.536364,0.15;0.363636x0.75)], dtype=object)
You can also pass a subset of columns to plot, as well as group by multiple columns:
In [897]: df = DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,3), columns=['Col1', 'Col2', 'Col3'])
In [898]: df['X'] = Series(['A','A','A','A','A','B','B','B','B','B'])
In [899]: df['Y'] = Series(['A','B','A','B','A','B','A','B','A','B'])
In [900]: plt.figure();
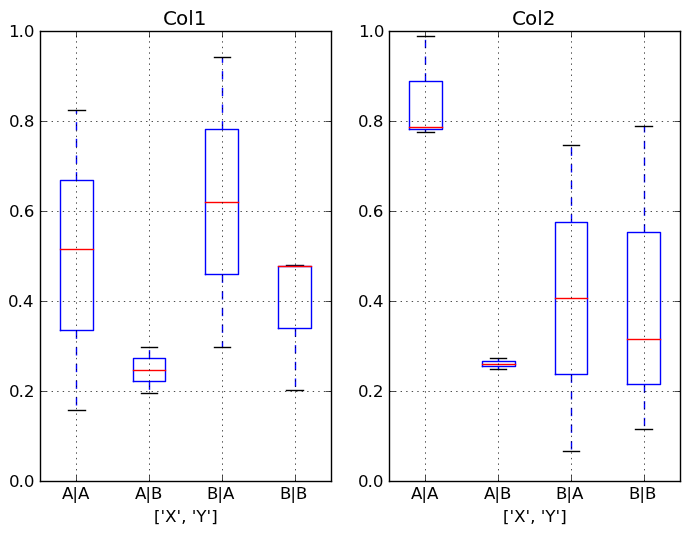
In [900]: df.boxplot(column=['Col1','Col2'], by=['X','Y'])
Out[900]: array([Axes(0.1,0.15;0.363636x0.75), Axes(0.536364,0.15;0.363636x0.75)], dtype=object)