pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.to_latex¶
- Styler.to_latex(buf=None, *, column_format=None, position=None, position_float=None, hrules=False, label=None, caption=None, sparse_index=None, sparse_columns=None, multirow_align='c', multicol_align='r', siunitx=False, encoding=None, convert_css=False)[source]¶
Write Styler to a file, buffer or string in LaTeX format.
New in version 1.3.0.
- Parameters
- bufstr, Path, or StringIO-like, optional, default None
Buffer to write to. If
None, the output is returned as a string.- column_formatstr, optional
The LaTeX column specification placed in location:
\begin{tabular}{<column_format>}
Defaults to ‘l’ for index and non-numeric data columns, and, for numeric data columns, to ‘r’ by default, or ‘S’ if
siunitxisTrue.- positionstr, optional
The LaTeX positional argument (e.g. ‘h!’) for tables, placed in location:
\begin{table}[<position>]
- position_float{“centering”, “raggedleft”, “raggedright”}, optional
The LaTeX float command placed in location:
\begin{table}[<position>]
\<position_float>
- hrulesbool, default False
Set to True to add \toprule, \midrule and \bottomrule from the {booktabs} LaTeX package.
- labelstr, optional
The LaTeX label included as: \label{<label>}. This is used with \ref{<label>} in the main .tex file.
- captionstr, tuple, optional
If string, the LaTeX table caption included as: \caption{<caption>}. If tuple, i.e (“full caption”, “short caption”), the caption included as: \caption[<caption[1]>]{<caption[0]>}.
- sparse_indexbool, optional
Whether to sparsify the display of a hierarchical index. Setting to False will display each explicit level element in a hierarchical key for each row. Defaults to
pandas.options.styler.sparse.indexvalue.- sparse_columnsbool, optional
Whether to sparsify the display of a hierarchical index. Setting to False will display each explicit level element in a hierarchical key for each row. Defaults to
pandas.options.styler.sparse.columnsvalue.- multirow_align{“c”, “t”, “b”}
If sparsifying hierarchical MultiIndexes whether to align text centrally, at the top or bottom.
- multicol_align{“r”, “c”, “l”}
If sparsifying hierarchical MultiIndex columns whether to align text at the left, centrally, or at the right.
- siunitxbool, default False
Set to
Trueto structure LaTeX compatible with the {siunitx} package.- encodingstr, default “utf-8”
Character encoding setting.
- convert_cssbool, default False
Convert simple cell-styles from CSS to LaTeX format. Any CSS not found in conversion table is dropped. A style can be forced by adding option –latex. See notes.
- Returns
- str or None
If buf is None, returns the result as a string. Otherwise returns None.
See also
Styler.formatFormat the text display value of cells.
Notes
Latex Packages
For the following features we recommend the following LaTeX inclusions:
Feature
Inclusion
sparse columns
none: included within default {tabular} environment
sparse rows
\usepackage{multirow}
hrules
\usepackage{booktabs}
colors
\usepackage[table]{xcolor}
siunitx
\usepackage{siunitx}
bold (with siunitx)
\usepackage{etoolbox}\robustify\bfseries\sisetup{detect-all = true} (within {document})italic (with siunitx)
\usepackage{etoolbox}\robustify\itshape\sisetup{detect-all = true} (within {document})Cell Styles
LaTeX styling can only be rendered if the accompanying styling functions have been constructed with appropriate LaTeX commands. All styling functionality is built around the concept of a CSS
(<attribute>, <value>)pair (see Table Visualization), and this should be replaced by a LaTeX(<command>, <options>)approach. Each cell will be styled individually using nested LaTeX commands with their accompanied options.For example the following code will highlight and bold a cell in HTML-CSS:
>>> df = pd.DataFrame([[1,2], [3,4]]) >>> s = df.style.highlight_max(axis=None, ... props='background-color:red; font-weight:bold;') >>> s.render()
The equivalent using LaTeX only commands is the following:
>>> s = df.style.highlight_max(axis=None, ... props='cellcolor:{red}; bfseries: ;') >>> s.to_latex()
Internally these structured LaTeX
(<command>, <options>)pairs are translated to thedisplay_valuewith the default structure:\<command><options> <display_value>. Where there are multiple commands the latter is nested recursively, so that the above example highlighed cell is rendered as\cellcolor{red} \bfseries 4.Occasionally this format does not suit the applied command, or combination of LaTeX packages that is in use, so additional flags can be added to the
<options>, within the tuple, to result in different positions of required braces (the default being the same as--nowrap):Tuple Format
Output Structure
(<command>,<options>)
\<command><options> <display_value>
(<command>,<options>
--nowrap)\<command><options> <display_value>
(<command>,<options>
--rwrap)\<command><options>{<display_value>}
(<command>,<options>
--wrap){\<command><options> <display_value>}
(<command>,<options>
--lwrap){\<command><options>} <display_value>
(<command>,<options>
--dwrap){\<command><options>}{<display_value>}
For example the textbf command for font-weight should always be used with –rwrap so
('textbf', '--rwrap')will render a working cell, wrapped with braces, as\textbf{<display_value>}.A more comprehensive example is as follows:
>>> df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2.2, "dogs"], [3, 4.4, "cats"], [2, 6.6, "cows"]], ... index=["ix1", "ix2", "ix3"], ... columns=["Integers", "Floats", "Strings"]) >>> s = df.style.highlight_max( ... props='cellcolor:[HTML]{FFFF00}; color:{red};' ... 'textit:--rwrap; textbf:--rwrap;' ... ) >>> s.to_latex()
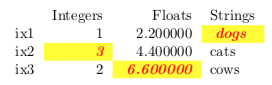
Table Styles
Internally Styler uses its
table_stylesobject to parse thecolumn_format,position,position_float, andlabelinput arguments. These arguments are added to table styles in the format:set_table_styles([ {"selector": "column_format", "props": f":{column_format};"}, {"selector": "position", "props": f":{position};"}, {"selector": "position_float", "props": f":{position_float};"}, {"selector": "label", "props": f":{{{label.replace(':','§')}}};"} ], overwrite=False)
Exception is made for the
hrulesargument which, in fact, controls all three commands:toprule,bottomruleandmidrulesimultaneously. Instead of settinghrulestoTrue, it is also possible to set each individual rule definition, by manually setting thetable_styles, for example below we set a regulartoprule, set anhlineforbottomruleand exclude themidrule:set_table_styles([ {'selector': 'toprule', 'props': ':toprule;'}, {'selector': 'bottomrule', 'props': ':hline;'}, ], overwrite=False)
If other
commandsare added to table styles they will be detected, and positioned immediately above the ‘\begin{tabular}’ command. For example to add odd and even row coloring, from the {colortbl} package, in format\rowcolors{1}{pink}{red}, use:set_table_styles([ {'selector': 'rowcolors', 'props': ':{1}{pink}{red};'} ], overwrite=False)
A more comprehensive example using these arguments is as follows:
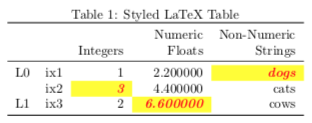
>>> df.columns = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([ ... ("Numeric", "Integers"), ... ("Numeric", "Floats"), ... ("Non-Numeric", "Strings") ... ]) >>> df.index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([ ... ("L0", "ix1"), ("L0", "ix2"), ("L1", "ix3") ... ]) >>> s = df.style.highlight_max( ... props='cellcolor:[HTML]{FFFF00}; color:{red}; itshape:; bfseries:;' ... ) >>> s.to_latex( ... column_format="rrrrr", position="h", position_float="centering", ... hrules=True, label="table:5", caption="Styled LaTeX Table", ... multirow_align="t", multicol_align="r" ... )
Formatting
To format values
Styler.format()should be used prior to calling Styler.to_latex, as well as other methods such asStyler.hide_index()orStyler.hide_columns(), for example:>>> s.clear() >>> s.table_styles = [] >>> s.caption = None >>> s.format({ ... ("Numeric", "Integers"): '\${}', ... ("Numeric", "Floats"): '{:.3f}', ... ("Non-Numeric", "Strings"): str.upper ... }) >>> s.to_latex() \begin{tabular}{llrrl} {} & {} & \multicolumn{2}{r}{Numeric} & {Non-Numeric} \\ {} & {} & {Integers} & {Floats} & {Strings} \\ \multirow[c]{2}{*}{L0} & ix1 & \\$1 & 2.200 & DOGS \\ & ix2 & \$3 & 4.400 & CATS \\ L1 & ix3 & \$2 & 6.600 & COWS \\ \end{tabular}
CSS Conversion
This method can convert a Styler constructured with HTML-CSS to LaTeX using the following limited conversions.
CSS Attribute
CSS value
LaTeX Command
LaTeX Options
font-weight
boldbolderbfseriesbfseriesfont-style
italicobliqueitshapeslshapebackground-color
red#fe01ea#f0ergb(128,255,0)rgba(128,0,0,0.5)rgb(25%,255,50%)cellcolor
{red}–lwrap[HTML]{FE01EA}–lwrap[HTML]{FF00EE}–lwrap[rgb]{0.5,1,0}–lwrap[rgb]{0.5,0,0}–lwrap[rgb]{0.25,1,0.5}–lwrapcolor
red#fe01ea#f0ergb(128,255,0)rgba(128,0,0,0.5)rgb(25%,255,50%)color
{red}[HTML]{FE01EA}[HTML]{FF00EE}[rgb]{0.5,1,0}[rgb]{0.5,0,0}[rgb]{0.25,1,0.5}It is also possible to add user-defined LaTeX only styles to a HTML-CSS Styler using the
--latexflag, and to add LaTeX parsing options that the converter will detect within a CSS-comment.>>> df = pd.DataFrame([[1]]) >>> df.style.set_properties( ... **{"font-weight": "bold /* --dwrap */", "Huge": "--latex--rwrap"} ... ).to_latex(convert_css=True) \begin{tabular}{lr} {} & {0} \\ 0 & {\bfseries}{\Huge{1}} \\ \end{tabular}