pandas.io.formats.style.Styler.background_gradient#
- Styler.background_gradient(cmap='PuBu', low=0, high=0, axis=0, subset=None, text_color_threshold=0.408, vmin=None, vmax=None, gmap=None)[source]#
Color the background in a gradient style.
The background color is determined according to the data in each column, row or frame, or by a given gradient map. Requires matplotlib.
- Parameters
- cmapstr or colormap
Matplotlib colormap.
- lowfloat
Compress the color range at the low end. This is a multiple of the data range to extend below the minimum; good values usually in [0, 1], defaults to 0.
- highfloat
Compress the color range at the high end. This is a multiple of the data range to extend above the maximum; good values usually in [0, 1], defaults to 0.
- axis{0, 1, “index”, “columns”, None}, default 0
Apply to each column (
axis=0or'index'), to each row (axis=1or'columns'), or to the entire DataFrame at once withaxis=None.- subsetlabel, array-like, IndexSlice, optional
A valid 2d input to DataFrame.loc[<subset>], or, in the case of a 1d input or single key, to DataFrame.loc[:, <subset>] where the columns are prioritised, to limit
datato before applying the function.- text_color_thresholdfloat or int
Luminance threshold for determining text color in [0, 1]. Facilitates text
visibility across varying background colors. All text is dark if 0, and
light if 1, defaults to 0.408.
- vminfloat, optional
Minimum data value that corresponds to colormap minimum value. If not specified the minimum value of the data (or gmap) will be used.
- vmaxfloat, optional
Maximum data value that corresponds to colormap maximum value. If not specified the maximum value of the data (or gmap) will be used.
- gmaparray-like, optional
Gradient map for determining the background colors. If not supplied will use the underlying data from rows, columns or frame. If given as an ndarray or list-like must be an identical shape to the underlying data considering
axisandsubset. If given as DataFrame or Series must have same index and column labels consideringaxisandsubset. If supplied,vminandvmaxshould be given relative to this gradient map.New in version 1.3.0.
- Returns
- Styler
See also
Styler.text_gradientColor the text in a gradient style.
Notes
When using
lowandhighthe range of the gradient, given by the data ifgmapis not given or bygmap, is extended at the low end effectively by map.min - low * map.range and at the high end by map.max + high * map.range before the colors are normalized and determined.If combining with
vminandvmaxthe map.min, map.max and map.range are replaced by values according to the values derived fromvminandvmax.This method will preselect numeric columns and ignore non-numeric columns unless a
gmapis supplied in which case no preselection occurs.Examples
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["City", "Temp (c)", "Rain (mm)", "Wind (m/s)"], ... data=[["Stockholm", 21.6, 5.0, 3.2], ... ["Oslo", 22.4, 13.3, 3.1], ... ["Copenhagen", 24.5, 0.0, 6.7]])
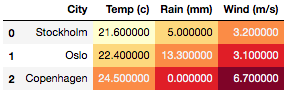
Shading the values column-wise, with
axis=0, preselecting numeric columns>>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=0)
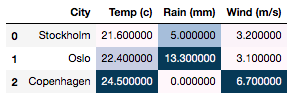
Shading all values collectively using
axis=None>>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=None)
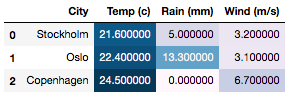
Compress the color map from the both
lowandhighends>>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=None, low=0.75, high=1.0)
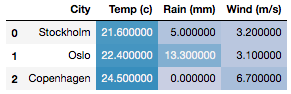
Manually setting
vminandvmaxgradient thresholds>>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=None, vmin=6.7, vmax=21.6)
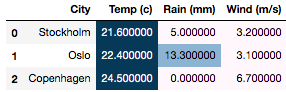
Setting a
gmapand applying to all columns with anothercmap>>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=0, gmap=df['Temp (c)'], cmap='YlOrRd') ...
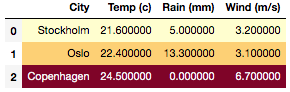
Setting the gradient map for a dataframe (i.e.
axis=None), we need to explicitly statesubsetto match thegmapshape>>> gmap = np.array([[1,2,3], [2,3,4], [3,4,5]]) >>> df.style.background_gradient(axis=None, gmap=gmap, ... cmap='YlOrRd', subset=['Temp (c)', 'Rain (mm)', 'Wind (m/s)'] ... )